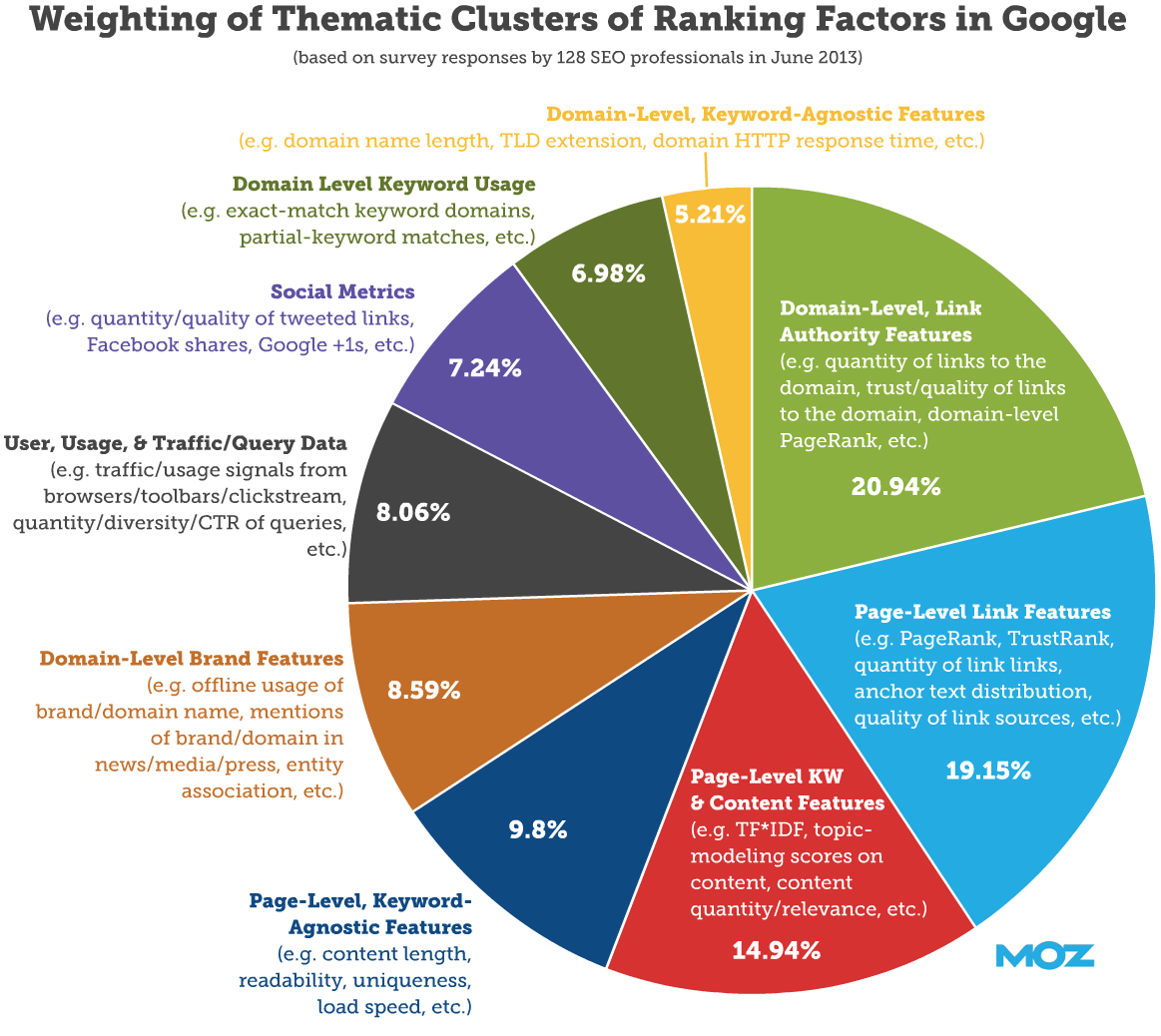
Off page SEO refers to techniques that can be used to improve the position of a web site in the search engine results page (SERPs). Many people associate off-page SEO with link building but it is not only that. In general, off Page SEO has to do with promotion methods – beyond website design –for the purpose of ranking a website higher in the search results.
Let’s take it from the beginning…
What is SEO?
Search engine optimization is the term used to describe a set of processes that aim in optimizing a website for search engines. SEO is important not only for getting high quality visitors from search, but it’s also a way to improve the user-friendliness of your website and increase its credibility.
Search engines are using complex algorithms to determine which pages to include in their index and the order they show these pages in the search results.
SEO is the way to ‘speak’ to search engines in a language they can understand and give them with more information about your website.
SEO has two major components, On Page and Off Page SEO.
On Page SEO
On Page SEO refers to settings you can apply on your website so that it is optimized for search engines. The most important On-Page SEO tips are:
Having optimized titles and descriptions
Proper URL Structures
User friendly navigation (breadcrumbs, user sitemaps)
Optimized internal links
Text Formatting (use of h1,h2,bold etc)
Image optimization (image size, proper image names, use of ALT tag)
User friendly 404 pages
Fast loading pages
Mobile Friendly pages
Top quality fresh content (This is always the most important SEO factor!)
External links (no broken links or links to ‘bad’ sites)
You can find out more details about all the above tips in the SEO Tips for beginners article.
Off Page SEO

Unlike On- page SEO, Off-page SEO refers to activities you can perform outside the boundaries of your website. The most important are:
Link Building
Social Media Marketing
Social bookmarking
We will examine these in more details below, but first let me explain about the importance and benefits of off-page SEO.
Why is Off-Page SEO important?
Search engines have been trying for decades to find a way to return the best results to the searcher.
To achieve this, they take into account the on-site SEO factors (described above), some other quality factors and off-page SEO.
Off Page SEO gives them a very good indication on how the World (other websites and users) perceive the particular website.
A web site that is high quality and useful is more likely to have references (links) from other websites; it is more likely to have mentions on social media (Facebook likes, tweets, Pins, +1’s etc.) and it is more likely to be bookmarked and shared among communities of like-minded users.
What are the benefits of ‘off-site SEO’ to website owners?
A successful off-site SEO strategy will generate the following benefits to website owners:
Increase in rankings – The website will rank higher in the SERPs and this also means more traffic.
More exposure – Higher rankings also means greater exposure because when a website ranks in the top positions: it gets more links, more visits and more social media mentions. It’s like a never ending sequence of events where one thing leads to another and then to another etc.
Link Building
Link building is the most popular and effective off-Page SEO method. Basically by building external links to your website, you are trying to gather as many ‘votes’ as you can, so that you can bypass your competitors and rank higher.
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU:
Running a WordPress website? Then download this how to guide and learn how to optimize your website like a Pro.
For example, if someone likes this article and references it from his/her website or blog, then this is like telling search engines that this page has good information.
Over the years webmasters have been trying to build links to their websites to get higher rankings and they ‘invented’ a number of ways to increase link count. The most popular ways were:
Blog Directories – something like yellow pages but each entry had a link pointing to a website.
Forum Signatures – Many people were commenting on forums for the sole purpose of getting a link back to their website (they included the links in their signature).
Comment link – The same concept as forum signatures where you would comment on some other website or blog in order to get a link back. Even worse, instead of using your real name you could use keywords so instead of writing ‘comment by Alex Chris’, you wrote ‘comment by How to lose weight’.
Article Directories – By publishing your articles in article directories you could get a link (or 2) back to your website. Some article directories accepted only unique content while other directories accepted anything from spin articles to already published articles.
Shared Content Directories – Websites like hubpages and infobarrel allowed you to publish content and in return you could add a couple of links pointing to your websites.
Link exchange schemes – Instead of trying to publish content you could get in touch with other webmasters and exchange links. In other words, I could link your website from mine and you could do the same.
In some cases you could even do more complicated exchanges by doing a 3-way link: I link to your website from my website but you link to my website from a different website.
Notice that I used the past tense to describe all the above methods because not only they do not work today, you should not even try them.
If you try to ‘trick’ search engines by building artificial links, you are more likely to get a penalty rather than an increase in rankings (especially when it comes to Google).
The birth of black hat SEO
Link building was an easy way to manipulate the search engine algorithms and many spammers tried to take advantage of this by building link networks which gradually lead to the creation of what is generally known as black hat SEO.
Google has become very intelligent in recognizing black hat techniques and with the introduction of Panda, Penguin and Hummingbird (that’s how the Google Algorithm releases are called), they have managed to solve the problem and protect their search engine results from spammers.
Of course there are still exceptions but they are doing advances in every new algorithmic release and soon enough none of these tricks will work.
To “follow” or “nofollow”
In addition to the above and in order to give webmasters a way to link to a website without passing any ‘link juice’ (for example in the case of ads), search engines introduced what is known as the “nofollow” link.
This is a special tag you can add to a link (for example: “<a href=http://www.somesite.com rel=”nofollow”>Some Site</a>) that tells search engines not to count the particular link as a ‘vote of trust’ to the referenced website.
This was done so that you can link to other websites from yours without taking the risk of being caught for selling or exchanging links.
As a rule of thumb, you should add the nofollow tag on all your external links (within your pages) that go to websites you cannot trust 100%, to ALL your comment links, to ALL your blogroll links and to ALL banner ad links.
What is a good link?
So, if the above links are not useful, what is a good link?
First, you should understand that link building it’s not only a matter of quantity but it is a matter of quality as well.
In other words, it no longer matters how many links are pointing to your website but it is more important from where these links are coming.
For example, a link from a normal blog does not have the same ‘weight’ as a link from New York Times or a link from Matt Cutts blog (former head of Google Quality team) is not the same as a link from my blog.
The obvious question is, how to you get these links?
If you ask Google they will tell you that any links pointing to your website has to be natural links. Natural links are exactly what their name implies. A website owner or blogger likes another website or blog and naturally adds a link to his/her blog.
Does this happen in reality or is it another myth?
It certainly does but you have to try really hard to get to this point. Take for example this blog, there are many incoming links because other webmasters find the content interesting and I also link to other sites in my articles because I find their content interesting and want to inform my readers about it.
This is natural link building, a link has more value from the reader’s’ point of view rather than the search engine’s point of view.
The best way to attract links is to publish link worthy content that other people would like to link to.
Social media is part of ‘off-site SEO’ and if you think about it, it’s also a form of link building. It should be noted that almost all of the links you get from social media sites are “nofollow” but this does not mean that they do not have any value.
Social Media mentions are gaining ground as ranking factors and proper configuration of social media profiles can also boost SEO.
Social Bookmarking
Social bookmarking is not as popular as it used to be in the past but it is still a good way to get traffic to your website. Depending on your niche you can find web sites like reddit.com, stumbleupon.com, scoop.it and delicious.com (to name a few) to promote your content.
Conclusion
Off-page SEO is as important as on-site SEO. If you want your SEO campaigns to be successful you have to do both. When thinking about link building don’t take the easy way, but try to get links from hard-to-get places. The more difficult is to get a link, the more value it has.
Digital Marketing Company in Lucknow.
Online Marketing Company in Lucknow.
Source


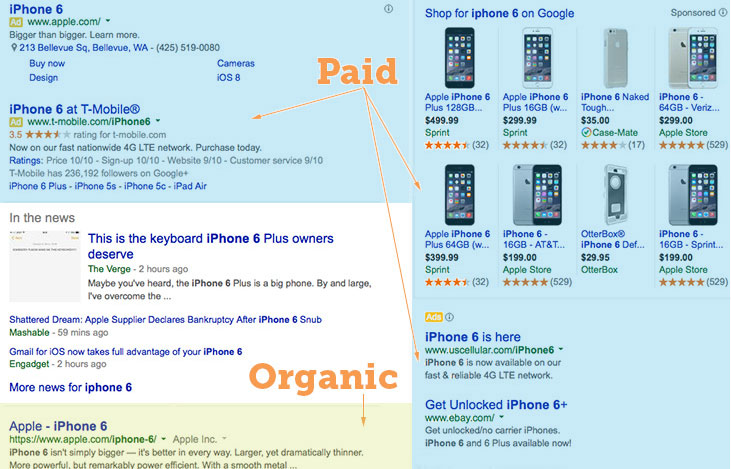 Organic se
Organic se